Abstract
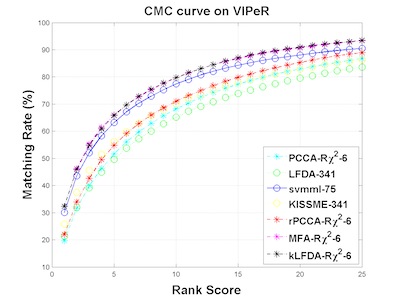
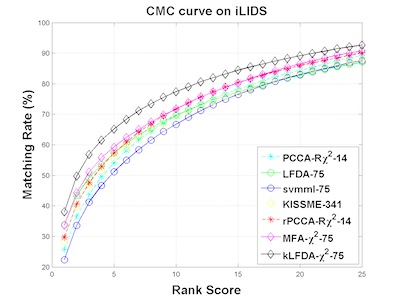
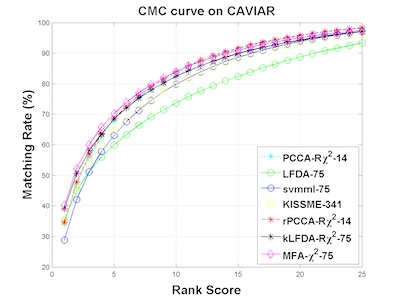
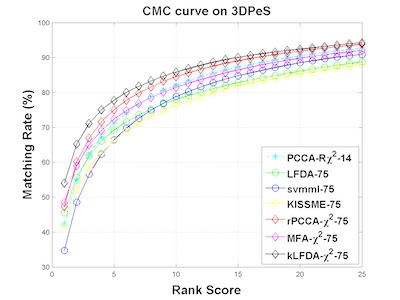
Re-identification of individuals across camera networks with limited or no overlapping fields of view remains challenging in spite of significant research efforts. In this paper, we propose the use, and extensively evaluate the performance, of four alternatives for re-ID classification: regularized Pairwise Constrained Component Analysis, kernel Local Fisher Discriminant Analysis, Marginal Fisher Analysis and a ranking ensemble voting scheme, used in conjunction with different sizes of sets of histogram-based features and linear, X2 and RBF-X2 kernels. Comparisons against the state-of-art show significant improvements in performance measured both in terms of Cumulative Match Characteristic curves (CMC) and Proportion of Uncertainty Removed (PUR) scores on the challenging VIPeR, iLIDS, CAVIAR and 3DPeS datasets.
New! Collection of most public re-id datasets
New! The latest version of code is available on github now!
Motivation
| Papers | KISSME | PCCA | LFDA | SVMML | Ours |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grid schema | 8X16 patches, 8X8 stride | 6 non-overlap strips | 8X8 patches, 4X4 stride | Hierarchical | 6 strips, 32X32, 16X16 or 8X8 patches |
| Feature channel | HSV, Lab, LBP | HSV, RGB, YUV, LBP | HSV, YUV | SIFT | RGB, HSV, YUV, LBP |
| Dimension reduction | PCA | N/A | PCA | Supervised PCA | N/A |
| Rank 1 results on VIPeR | 19.60% | 19.27% | 24.18% | 30.00% | 35.10% |
Metric Learning Methods in Re-ID
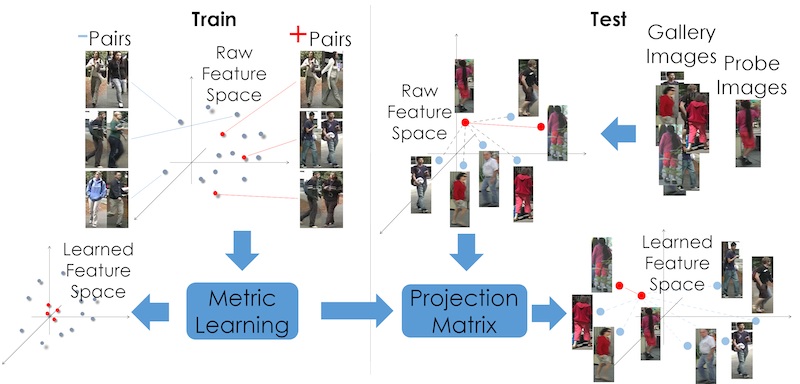
This work forcus on approaches designing classifiers to learn specialized metrics, that enforce features from the same individual to be closer than features from different individuals.
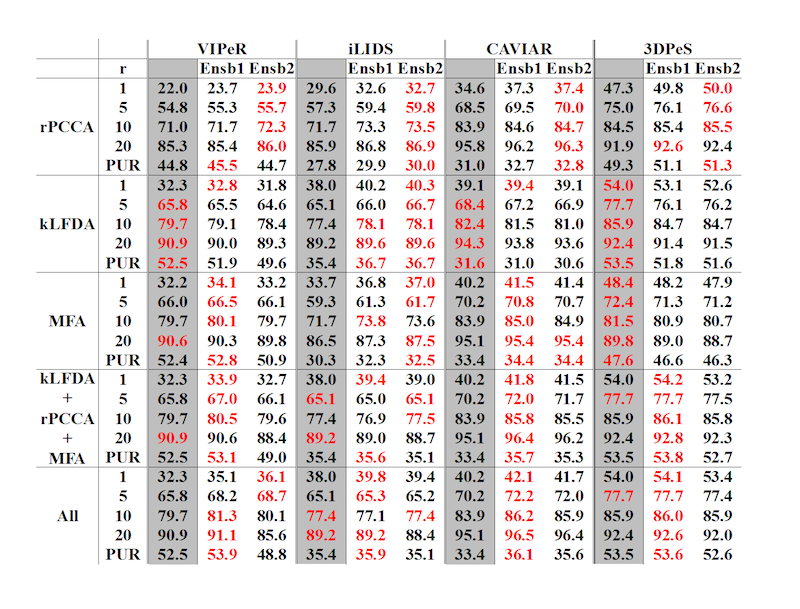
Improving Performance by Fusing Algorithms
Publication
X. Fei, M. Gou, O. Camps and M. Sznaier: "Person Re-Identification using Kernel-based Metric Learning Methods". In ECCV 2014.